The Potential Use of Anethole in Oral Cancer Treatment
Oral cancer is among the world’s important public health issues. The conventional treatments for oral cancer rely heavily on surgery, chemo- and radiotherapy. Although they are efficient, they have significant adverse effects limiting their use. Indeed, many bioactive compounds derived from flavored plants have been reported to have anticancer properties, high levels of cytotoxicity toward cancer cells, and low ones toward normal cells. Therefore, it is paramount to identify natural products that do protect and prevent against oral cancer in the purpose to supply new pharmacological treatments. Our current study aims to explore the antitumor properties of anethole, 1-methoxy-4-[(E)-1-propenyl]-benzene, a compound extracted from fennel or star anise, to investigate its chemopreventive or therapeutic effect against oral cancer.
Results
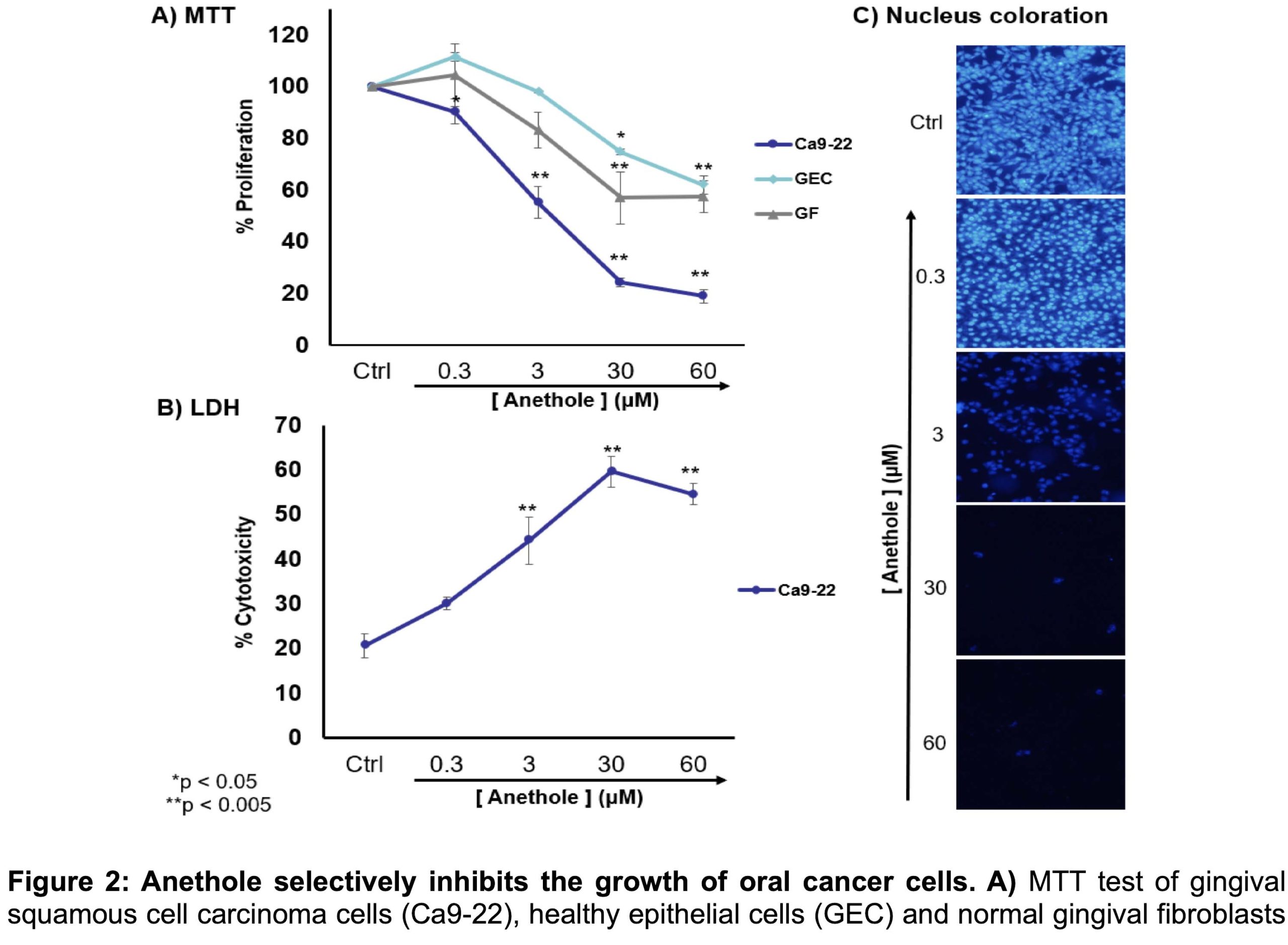
Anethole selectively inhibits the proliferation of oral cancer cells by:
- modulation of the expression of several oncoproteins (e.g. Cycline D1, p53)
- inhibition of proliferative pathways (MAPKase, Wnt and NF- κB)
Anethole induces apoptosis of oral cancer cells by:
- inhibition of caspase 3 and caspase 9
- PARP1 cleavage
Anethole exercises its anticancer capacity by:
- its invasion / migration capacity
- Inhibition of the epithelio-mesenchymal transition
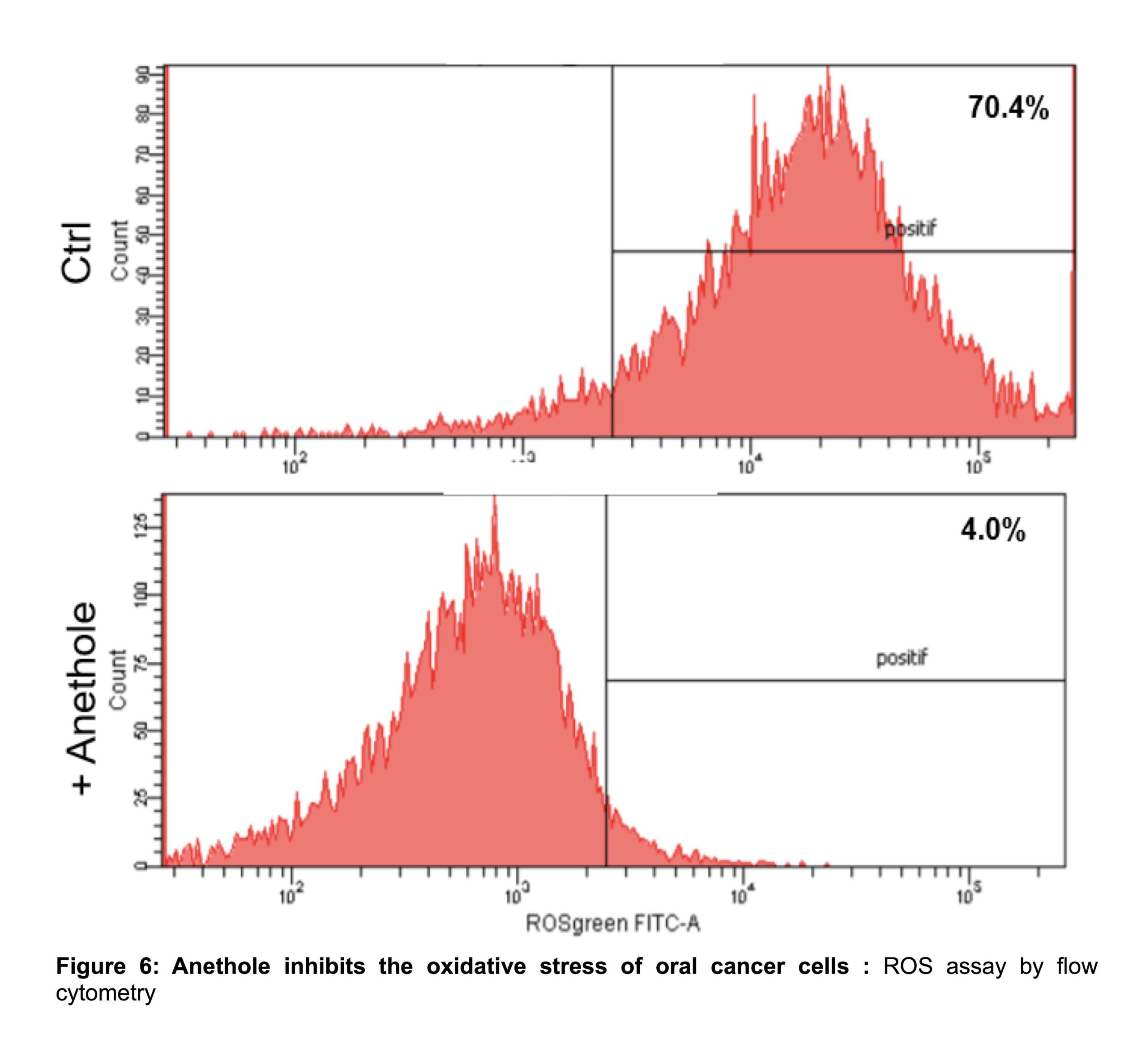
Anethole inhibits the oxidative stress by :
- Decrease ROS
- Activate GSH
Anethole could be a new, powerful chemotherapeutic agent for oral cancer.
Équipe de recherche et collaborateurs
- Principal Investigator: Abdelhabib Semlali
- Student: Camille Contant
- Co-Investigator: Mahmoud Rouabhia et Fatiha Chandad
- Collaborator: Lionel Loubaki, Héma-Québec

